What is weight loss surgery, and how many types are there?

Weight loss surgery, also known as bariatric surgery, is a procedure aimed at reducing the size of the stomach, thereby limiting food intake and facilitating weight loss. Some surgeries also alter the digestive process, affecting nutrient absorption and reducing appetite by removing parts of the stomach that produce hunger hormones, leading to reduced food intake and, consequently, weight loss.
Who is it for?
- Individuals with a BMI of 32.5 and above, coupled with chronic conditions like type 2 diabetes, high blood pressure, and others.
- Those with a BMI of 37.5 and above, even without underlying health issues.
- Individuals who have tirelessly tried traditional weight loss methods, like diet and exercise, only to find them ineffective.
There are six main types of weight loss surgery, each with its unique approach and benefits.
1. Sleeve gastrectomy
- Removes 80% of the outer stomach and eliminates the top part (Fundus), reducing Ghrelin production and hunger after surgery, leading to reduced food intake.
- Can lead to a 60% reduction in excess weight within a year.
- Alleviates conditions like diabetes, high blood fat, high blood pressure, sleep apnea, and ovarian cysts causing hirsutism and irregular menstruation.
- Allows for future stomach examination via endoscopy if needed.
- Quick surgical procedure.
- Unsuited for individuals with severe acid reflux.
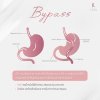
2. Gastric bypass surgery
- Changes the digestive tract by dividing the stomach into two parts: a small pouch (about 30 cc) and a larger portion. It connects the middle part of the small intestine to the small pouch, redirecting food to bypass the larger portion of the stomach.
- Food bypasses the larger portion of the stomach and goes straight to the middle part of the small intestine.
The remaining stomach is left in the body, making future stomach examination via endoscopy not possible.
- Post-surgery results in reduced food intake and nutrient absorption because most of the stomach is removed and the digestive tract is significantly altered, leading to weight loss.
- Can reduce excess weight by approximately 60-70% within one year and improve various health conditions, including severe diabetes.
- Takes longer to perform compared to sleeve surgery.
- Suitable for individuals with severe diabetes or severe acid reflux.
- Reduces the possibilities of other surgical procedures in the future.
3. Adjustable gastric banding (lap band surgery)
- Involves placing a band around the stomach to reduce its size.
- The gastric band method is less recommended due to controversy over its effectiveness for weight loss and can cause issues like slipping or breaking of the gastric band, and more vomiting.
4. Gastric balloon procedures
- Balloon insertion is a non-surgical procedure.
It entails inserting a balloon through the mouth, down the oesophagus, and into the stomach. Once in place, the balloon is inflated to occupy space in the stomach.
- This creates a sensation of fullness, which helps decrease food intake and leads to weight loss.
- The balloon remains in the stomach for up to one year.
- Upon removal, there's a risk of weight regain if eating habits return to previous levels.
Regardless of your body mass index meeting the criteria for weight loss surgery and reducing various diseases, it is advisable to consult a physician to choose the most appropriate method.
5. Sleeve+ gastrectomy
- Combination of elements from both sleeve gastrectomy and bypass surgery.
- Initially, the procedure involves performing gastric sleeve surgery. Subsequently, only the small intestine is bypassed, preventing food from passing through the duodenum and limiting nutrient absorption.
- Post-surgery, patients experience reduced food intake from the sleeve surgery and decreased nutrient absorption from the bypassed small intestine, resulting in weight loss.
- This approach aims to address long-term malnutrition issues often associated with bypass surgery and reduce the occurrence of stomach ulcers commonly observed post-bypass surgery.
- Reports suggest that this combined approach can achieve approximately 60-75% reduction in excess weight within one year and alleviate severe diabetes.
6. Endostitch
- A relatively new technique in Thailand, however it has already been in practice for sometime.